数据预处理:特征选择
发布时间:2021-12-03
公开文章
过滤式特征选择VarianceThreshold
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold,SelectKBest,f_classif
def test_VarianceThreshold():
'''
测试 VarianceThreshold 的用法
:return: None
'''
X=[[100,1,2,3],
[100,4,5,6],
[100,7,8,9],
[101,11,12,13]]
selector=VarianceThreshold(1)
selector.fit(X)
print("Variances is %s"%selector.variances_)
print("After transform is %s"%selector.transform(X))
print("The surport is %s"%selector.get_support(True))
print("After reverse transform is %s"%
selector.inverse_transform(selector.transform(X)))
test_VarianceThreshold()
Variances is [ 0.1875 13.6875 13.6875 13.6875]
After transform is [[ 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6]
[ 7 8 9]
[11 12 13]]
The surport is [1 2 3]
After reverse transform is [[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 0 4 5 6]
[ 0 7 8 9]
[ 0 11 12 13]]
def test_SelectKBest():
'''
测试 SelectKBest 的用法,其中考察的特征指标是 f_classif
:return: None
'''
X=[ [1,2,3,4,5],
[5,4,3,2,1],
[3,3,3,3,3,],
[1,1,1,1,1] ]
y=[0,1,0,1]
print("before transform:",X)
selector=SelectKBest(score_func=f_classif,k=3) # k=3
selector.fit(X,y)
print("scores_:",selector.scores_)
print("pvalues_:",selector.pvalues_)
print("selected index:",selector.get_support(True))
print("after transform:",selector.transform(X))
test_SelectKBest()
before transform: [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [5, 4, 3, 2, 1], [3, 3, 3, 3, 3], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]
scores_: [0.2 0. 1. 8. 9. ]
pvalues_: [0.69848865 1. 0.42264974 0.10557281 0.09546597]
selected index: [2 3 4]
after transform: [[3 4 5]
[3 2 1]
[3 3 3]
[1 1 1]]包裹式特征选择RFE,RFECV
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE,RFECV
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
def test_RFE():
'''
测试 RFE 的用法,其中目标特征数量为 2
:return: None
'''
iris=load_iris()
X=iris.data
y=iris.target
estimator=LinearSVC()
selector=RFE(estimator=estimator,n_features_to_select=2)
selector.fit(X,y)
print("N_features %s"%selector.n_features_)
print("Support is %s"%selector.support_)
print("Ranking %s"%selector.ranking_)
def test_RFECV():
'''
测试 RFECV 的用法
:return: None
'''
iris=load_iris()
X=iris.data
y=iris.target
estimator=LinearSVC()
selector=RFECV(estimator=estimator,cv=3)
selector.fit(X,y)
print("N_features %s"%selector.n_features_)
print("Support is %s"%selector.support_)
print("Ranking %s"%selector.ranking_)
print("Grid Scores %s"%selector.grid_scores_)
def test_compare_with_no_feature_selection():
'''
比较经过特征选择和未经特征选择的数据集,对 LinearSVC 的预测性能的区别
:return: None
'''
### 加载数据
iris=load_iris()
X,y=iris.data,iris.target
### 特征提取
estimator=LinearSVC()
selector=RFE(estimator=estimator,n_features_to_select=2)
X_t=selector.fit_transform(X,y)
#### 切分测试集与验证集
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X, y,
test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=y)
X_train_t,X_test_t,y_train_t,y_test_t=train_test_split(X_t, y,
test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=y)
### 测试与验证
clf=LinearSVC()
clf_t=LinearSVC()
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
clf_t.fit(X_train_t,y_train_t)
print("Original DataSet: test score=%s"%(clf.score(X_test,y_test)))
print("Selected DataSet: test score=%s"%(clf_t.score(X_test_t,y_test_t)))
test_RFE() # 调用 test_RFE
N_features 2
Support is [False True False True]
Ranking [3 1 2 1]
test_compare_with_no_feature_selection() # 调用 test_compare_with_no_feature_selection
Original DataSet: test score=0.9473684210526315
Selected DataSet: test score=0.9473684210526315
test_RFECV() # 调用 test_RFECV
N_features 4
Support is [ True True True True]
Ranking [1 1 1 1]
Grid Scores [0.91421569 0.94689542 0.95383987 0.96691176]嵌入式特征选择
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits,load_diabetes
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso
def test_SelectFromModel():
'''
测试 SelectFromModel 的用法。
:return: None
'''
digits=load_digits()
X=digits.data
y=digits.target
estimator=LinearSVC(penalty='l1',dual=False)
selector=SelectFromModel(estimator=estimator,threshold='mean')
selector.fit(X,y)
selector.transform(X)
print("Threshold %s"%selector.threshold_)
print("Support is %s"%selector.get_support(indices=True))
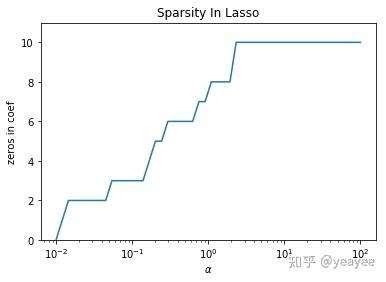
def test_Lasso(*data):
'''
测试 alpha 与稀疏性的关系
:param data: 可变参数。它是一个元组,这里要求其元素依次为:训练样本集、测试样本集、训练样本的值、测试样本的值
:return: None
'''
X,y=data
alphas=np.logspace(-2,2)
zeros=[]
for alpha in alphas:
regr=Lasso(alpha=alpha)
regr.fit(X,y)
### 计算零的个数 ###
num=0
for ele in regr.coef_:
if abs(ele) < 1e-5:num+=1
zeros.append(num)
##### 绘图
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.plot(alphas,zeros)
ax.set_xlabel(r"$\alpha$")
ax.set_xscale("log")
ax.set_ylim(0,X.shape[1]+1)
ax.set_ylabel("zeros in coef")
ax.set_title("Sparsity In Lasso")
plt.show()
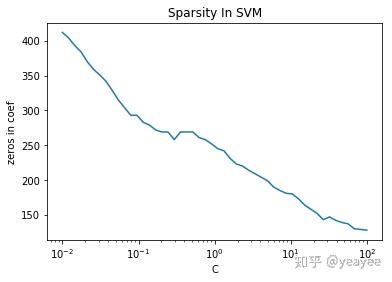
def test_LinearSVC(*data):
'''
测试 C 与 稀疏性的关系
:param data: 可变参数。它是一个元组,这里要求其元素依次为:训练样本集、测试样本集、训练样本的标记、测试样本的标记
:return: None
'''
X,y=data
Cs=np.logspace(-2,2)
zeros=[]
for C in Cs:
clf=LinearSVC(C=C,penalty='l1',dual=False)
clf.fit(X,y)
### 计算零的个数 ###
num=0
for row in clf.coef_:
for ele in row:
if abs(ele) < 1e-5:num+=1
zeros.append(num)
##### 绘图
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.plot(Cs,zeros)
ax.set_xlabel("C")
ax.set_xscale("log")
ax.set_ylabel("zeros in coef")
ax.set_title("Sparsity In SVM")
plt.show()
test_SelectFromModel() # 调用 test_SelectFromModel
Threshold 0.6759827221334211
Support is [ 2 3 4 5 6 9 12 13 14 18 19 20 21 22 26 27 30 33 36 38 41 42 43 44
45 51 53 54 55 58 61]
data=load_diabetes() # 生成用于回归问题的数据集
test_Lasso(data.data,data.target) # 调用 test_Lasso
data=load_digits() # 生成用于分类问题的数据集
test_LinearSVC(data.data,data.target) # 调用 test_LinearSVC